1 Introduction Due to the characteristics of high precision, high speed, high efficiency, and safety and reliability, CNC machine tools are rapidly gaining popularity in enterprises in the renewal of manufacturing technology and equipment. A CNC machine is an automated machine equipped with a program control system that allows the machine to move and process parts based on programmed programs. It combines the latest technologies in machinery, automation, computer, measurement, and microelectronics, and uses a variety of sensors. This article describes the application of various sensors on CNC machine tools. 2 Sensor Introduction A sensor is a device or device that can sense a specified measurement and convert it into a usable output signal according to a certain law. The input signal (measured) is often non-electricity, and the output signal is often an easily-processable quantity of electricity, such as voltage. There are many kinds of sensors, and the classification standards are different. The name is not the same. Common resistance sensors, inductive sensors, capacitive sensors, temperature sensors, piezoelectric sensors, Hall sensors, thermocouple sensors, photoelectric sensors, digital Position sensors, etc. The sensors used in CNC machine tools include photoelectric encoders, linear encoders, proximity switches, temperature sensors, Hall sensors, current sensors, voltage sensors, pressure sensors, liquid level sensors, resolvers, inductive synchronizers, and speed sensors. Mainly used to detect position, linear displacement and angular displacement, speed, pressure, temperature and so on. 3 Requirements of Sensors for CNC Machine Tools (1) High reliability and strong anti-interference; Different kinds of CNC machine tools have different requirements for sensors. In general, large-scale machine tools require high speed response, and medium-sized and high-precision CNC machine tools mainly require precision. 4 Displacement detection The sensors for displacement detection mainly include pulse encoders, linear encoders, rotary transformers, and inductive synchronizers. 4.1 Pulse Encoder Application A pulse encoder is an angular displacement (rotational speed) sensor that can turn mechanical angles into electrical pulses. Pulse encoder can be divided into three types: photoelectric, contact and electromagnetic. Among them, there are many photoelectric applications. In Figure 1, the end of the X-axis and Z-axis are equipped with photoelectric encoders for angular displacement measurement and digital speed measurement. The angular displacement can indirectly reflect the linear displacement of the carriage or tool holder through the lead screw pitch. Linear gratings are made using the transmission and reflection of light. They are often used for displacement measurement, have high resolution, and have higher measurement accuracy than optical encoders and are suitable for dynamic measurements. In the feed drive, the grating scale is fixed on the bed, and the generated pulse signal directly reflects the actual position of the carriage. The servo system that uses the grating to detect the position of the table is a closed-loop control system. 4.3 Application of Resolver A resolver is an inductive micromotor with a continuous function of output voltage and angular displacement. The resolver consists of a stator and a rotor. Specifically, it consists of a core, two stator windings, and two rotor windings. The primary and secondary windings are placed on the stator and rotor, respectively, and electromagnetic coupling between the primary and secondary windings is performed. The degree relates to the rotation angle of the rotor. 4.4 Induction Synchronizer Application Induction synchronizer is made by using the principle that the mutual inductance of two planar windings varies with position. Its function is to convert the angle or linear displacement into the phase or amplitude of the induced electromotive force, which can be used to measure straight line or angular displacement. According to its structure can be divided into two kinds of linear and rotary. The linear induction synchronizer is composed of a fixed length and a sliding rule. The fixed length is installed on the machine bed. The sliding rule is installed on the moving part and moves along with the worktable. The stator of the rotary induction synchronizer is a fixed disc. Rotor For rotating discs. Induction synchronizer has the advantages of high precision and resolution, strong anti-interference ability, long service life, simple maintenance, long distance displacement measurement, good processability, and low cost. Linear inductive synchronizer is widely used in static displacement and dynamic measurement of large displacements, such as coordinate measuring machines, programmable CNC machine tools, high-precision heavy machine tools, and machining center measuring devices. Rotary induction synchronizers are widely used in turntables of machine tools and instruments as well as various rotary servo control systems. 5 position detection The position sensor can be used to detect the position and reflect the switch of a certain state, which is different from the displacement sensor. There are two kinds of contact sensors: proximity and proximity. 5.1 Contact Sensor Applications Contact of the contact sensor is actuated by two objects in contact with each other. There are trip switches, two-dimensional matrix position sensors and the like. The trip switch has a simple structure, reliable operation and low price. When an object touches the limit switch during the movement, the internal contacts will act to complete the control. For example, the travel switch can be controlled at both ends of the machining center in the X, Y, and Z directions, and the movement can be controlled. range. The two-dimensional matrix position sensor is installed on the inside of the palm of the hand and detects the contact position between itself and an object. 5.2 Application of proximity switches The proximity switch is a switch that can send an "action" signal when the object is close to a set distance, and it does not need to be in direct contact with the object. There are many kinds of proximity switches, mainly self-inductance, differential transformer type, eddy current type, capacitance type, reed switch, Hall type and so on. The application of proximity switches in CNC machine tools is mainly the knife holder selection control, the table stroke control, the cylinder and cylinder piston stroke control and so on. In toolholder selection control, as shown in Figure 2, the four cams from left to right correspond to the proximity switches SQ4 to SQ1 to form a four-bit binary code, and each code corresponds to one tool bit, for example, 0110 corresponds to No. 6 Tool position; Proximity switch SQ5 is used for parity checking to reduce errors. Every time the tool post rotates one tool position, it sends out a signal. This signal is compared with the tool position command of the numerical control system. When the tool position signal of the tool holder matches the command tool position signal, the tool selection is completed. figure 2 6 speed detection A speed sensor is a sensor that converts speed into an electrical signal. It can detect both linear and angular speeds. Commonly used are tachogenerators and pulse encoders. Tachometer generators have the following characteristics: (1) The output voltage and speed are strictly linear; (2) The slope of output voltage and speed ratio is large. Can be divided into two types of AC and DC. The pulse encoder generates a pulse when it is displaced by a unit of angle, and a timer can detect the angular velocity. In CNC machine tools, the speed sensor is generally used for the speed detection of the servo unit of the CNC system. 7 Pressure Detection The pressure sensor is a sensor that converts pressure into electrical signals. According to the working principle, it can be divided into piezoelectric sensors, piezoresistive sensors and capacitive sensors. It is a general term for detecting the energy of interaction among all substances such as gases, liquids, solids, etc. It also includes pressure gauges for measuring above atmospheric pressure and vacuum gauges for measuring subatmospheric pressure. The capacitance of the capacitive pressure sensor is determined by the area of ​​the electrode and the distance between the two electrodes. The characteristics of high sensitivity, good temperature stability, and large pressure range have recently been rapidly developed. In CNC machine tools, it can be used to detect the workpiece clamping force. When the clamping force is less than the set value, it will cause the workpiece to loosen, and the system will issue an alarm and stop the knife. In addition, a pressure sensor can also be used to detect the change in cutting force of the turning tool. In addition, it is also used in the lubrication system, hydraulic system, and pneumatic system to detect the pressure in the oil or air circuit. When the pressure in the oil or air circuit is lower than the set value, the contacts will move, and The fault signal is sent to the CNC system. 8 Temperature detection A temperature sensor is a device that converts the temperature into a resistance value or other electrical signal. Commonly used are platinum, copper-based thermal resistance sensors, semiconductor-based thermistor sensors and thermocouple sensors. On CNC machine tools, temperature sensors are used to detect temperature for temperature compensation or over-temperature protection. In the process of processing, the rotation of the motor, the movement of moving parts, cutting, etc. will generate heat, and the temperature distribution is not uniform, resulting in temperature difference, so that the CNC machine tool generates thermal deformation, affecting the part machining accuracy, in order to avoid the impact of temperature, can be Some parts of the CNC machine tools are equipped with temperature sensors, which sense the temperature signals and convert them into electrical signals for transmission to the CNC system for temperature compensation. In addition, a temperature sensor should be buried in a place where the motor needs to be overheated, and when it is overheated, it can be overheated by a numerical control system. 9 Tool Wear Monitoring Tool wear to a certain degree affects the dimensional accuracy and surface roughness of the workpiece. Therefore, tool wear is monitored. When the tool wears, the load on the spindle motor of the machine tool increases, the current and voltage of the motor also changes, the power changes accordingly, and the power change can be detected by the Hall sensor. When the power changes to a certain extent, the CNC system sends out an alarm signal and the locomotive stops running. At this time, the tool should be adjusted or replaced in time. 10 Conclusion The application of the sensors described above on CNC machine tools is the current situation, but with the development of sensors and CNC machine tools, some sensors will be eliminated, such as rotary transformers, and new sensors will continue to emerge, which will make CNC machine tools more perfect. , more adaptive. Plastic Raw Material Mixer,Granular materials mixer,Mixing of raw materials ,Pellet mixer CHANGLONGXING SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY (SHENZHEN) CO.,LTD , https://www.clxmachinery.com
(2) Meet the accuracy and speed requirements;
(3) Easy to use and maintain, suitable for machine tool operating environment;
(4) Low cost. 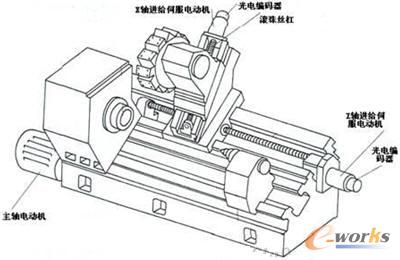
figure 1
4.2 Linear Grating Applications 
Hall sensors are sensors made using the Hall phenomenon. When semiconductors such as germanium are placed in a magnetic field and a current is applied in one direction, a potential difference occurs in the vertical direction. This is the Hall phenomenon. The small magnet is fixed on the moving part. When the part is close to the Hall element, a Hall phenomenon is generated to judge whether the object is in place.